設定您的資訊:
- 設定資訊
git config --global user.name "您的名字"git config --global user.email "您的電郵" - 移除資訊
git config --global --remove-section user.namegit config --global --remove-section user.email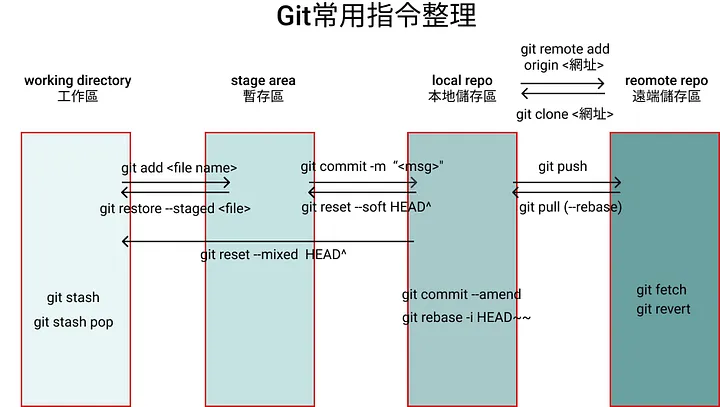
基本命令:
建立一個 Git 倉庫
git init
檢查哪些檔案可以新增到您的倉庫
git status
告訴 Git 要將哪些檔案納入版本控制(避免新增機密資訊,例如 API 金鑰、資料庫密碼等)
git add <~/your/files/path/first_file> <~/your/files/path/second_file>
git add . # **將所有檔案納入版本控制**
提交所有已新增的檔案,並附上訊息
git commit -m "您想新增的訊息"
新增遠端倉庫需要兩個參數:
- 遠端名稱,例如 'origin'
- 遠端 URL,例如 'https://github.com/username/repo.git'
git remote add origin <https://url/owner.repo.git>
從伺服器複製現有的 Git 倉庫到本機
- URL 方法:
git clone <https://url/owner.repo.git> <重新命名的名稱> - SSH 方法:
git clone <[email protected]:username/projectname.git>
將程式碼和檔案從本機推送到遠端
git push -u origin <branch>
如何設定遠端
- 檢查 Git 遠端資訊
git remote -v - 什麼是 upstream
- "upstream" 是指某個分支所建立的主分支。
- Git 預設使用 "origin" 作為遠端名稱。
- 設定遠端 upstream URL
git remote set-url upstream <https://url/owner.repo.git>
其他命令
檢查程式碼差異
git diff <file>
取得所有本機可用的資訊
git status